NCERT Class 6 Civics Chapter 3 Notes for quick revision from the chapter – “What is Government?”. NCERT Class 6 Civics Chapter 3 Notes cover all the important topics in a simplified and precise way.

What is Government?
A government is a system or group of people which takes care of a country, state, city, or village. The government takes care of the people by working for their welfare.
> The government takes decisions, makes plans, and then implements them.
> The government also makes laws, rules, and regulations to maintain law and order in its area of rule.
> The Government has the power to enforce its decisions and laws.
Levels of Government
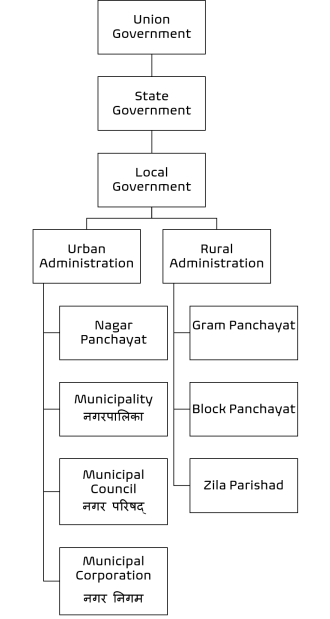
India is a huge country. To govern such a big country, the responsibilities have been divided into three levels. It means that the government works at three levels.
National Level – Union or Central Government
State Level – State Government
Local Level – Local Government
Local government has two types:
(1) Panchayati Raj (Rural Area)
(2) Municipal Council (Urban Area)
NCERT Class 6 Civics Chapter 3 Notes
Administrative Division of India
India 🡺 States 🡺 Districts 🡺 Blocks 🡺 Cities & Villages
Responsibilities of a Government
There are many responsibilities of the Government. A few of them are mentioned below.
> To provide basic facilities of health, education, transport, electricity, water, etc. to the people.
> To build public places and maintain them.
> To make development plans and execute them.
> To protect the boundaries of the country and maintain friendly relations with neighboring countries.
> To solve social issues like poverty, illiteracy, etc.
Types of Government
There are two main types of government based on the power to make decisions.
(1) Democracy
>A government system where people have the power to choose their leaders and these leaders become part of the government.
Hence, people have the power to form the government.
(2) Monarchy
>A government system where a king or a queen has the power to make decisions. People don’t participate in the government.
Democracy vs Monarchy
| Democracy | Monarchy |
|---|---|
| The government is formed by the people through elections. | King or a queen is not elected as there is no election conducted. |
| The government is elected for a fixed term. | The Crown is transferred to the next generation. |
| People indirectly participate in making the laws. | Only the monarch makes the laws. |
| The rule is done by the elected leaders. | Only the royal family rule. |
| People can ask questions to the government. | People may not have the right to ask questions. |
| All people are considered equal and given fundamental rights. | People may not be considered equal and may not have any rights. |
| Examples: India, USA, etc. | Examples: Saudi Arabia, UAE, etc. |

